Feature Engineering for Improving Model Prediction in Multiclass Text Classification
September 29, 2019
Introduction
‘Friends’ is one of my all time favorite TV shows. I was looking for a personal project to apply NLP, and thought it would be interesting to see how machine learning models can be trained to guess the characters from the show. I thought that data analysis and machine learning could be an interesting approach for an author/director to check if the cast members in their story or plot have predicatable traits or how their roles are being perceived by the audience.
My goal of writing this blog is to highlight that getting accurate prediction for an ML problem does not necessarily rely on the use of trying different ML models first. For problems related to classification, confusion matrix or roc_auc curve can be an useful guide to understand how simple feature engineering (i.e. as trivial as adding an additional feature) or resampling can improve prediction accuracy for linear ML models.
Data Processing
I scraped the data from the text transcripts for all episodes of Friends using Python’s Beautiful Soup4 Package. After parsing the data, removing blank spaces and non-relevant texts and concatenating the files, data was finally stored in a dataframe layout where every line said by a character, the corresponding episode and season were saved as an observation for input and the name of the cast members was saved as the output variable. Then I used the nltk package to tokenize the sentences into words, removed stop words (e.g. the’, ‘is’, ‘are’ etc.), punctuations, numbers and then lemmatized all the words to their basic forms(e.g. ‘walk’, ‘walked’, ‘walks’, ‘walking’ is converted to the basic form - ‘walk’).
Visualization
The bar plot below shows that the tv series has 304 characters in total. Count plot of number of lines for different characters suggests that the plots through the tv series are mainly centered around the main characters we already know (No Surprise!). All the main characters (i.e. Rachel, Ross, Joey, Phoebe, Chandler and Monica) have at least > 6000 lines in the show with Rachel and Ross taking the lead.
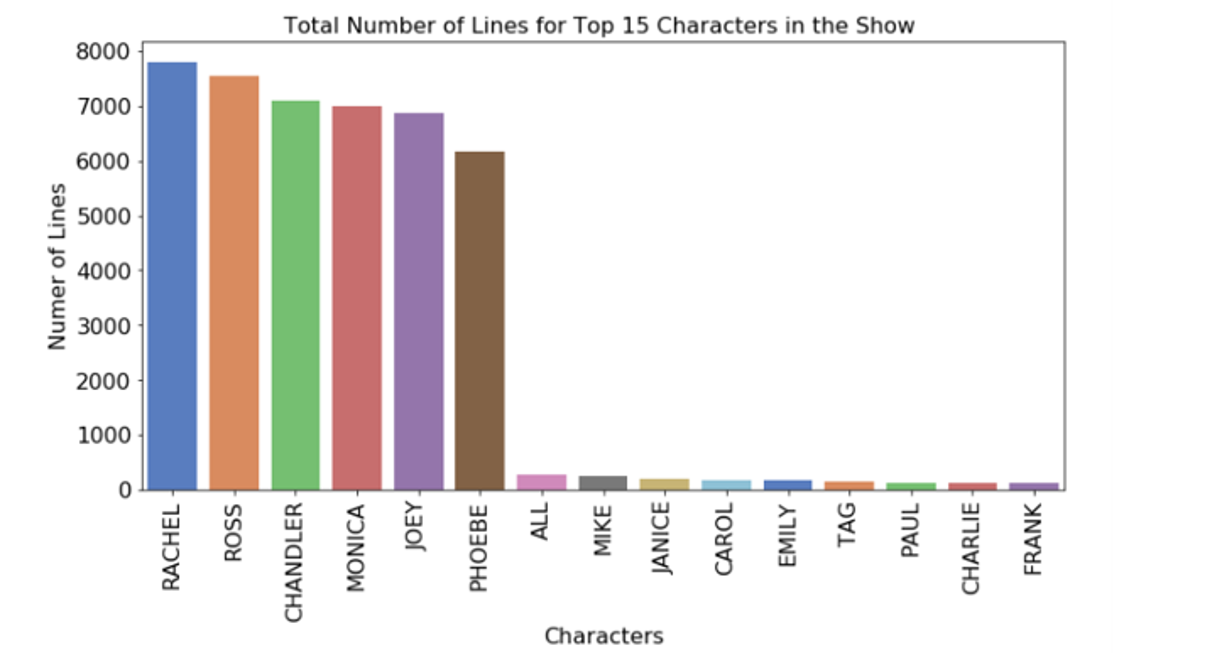
All the supporting actors have significantly fewer number of lines (<500) compared to the main characters. This implies that multiclass ML modeling may suffer from imbalance in the dataset when number of classes considered is > 6 in the analysis.
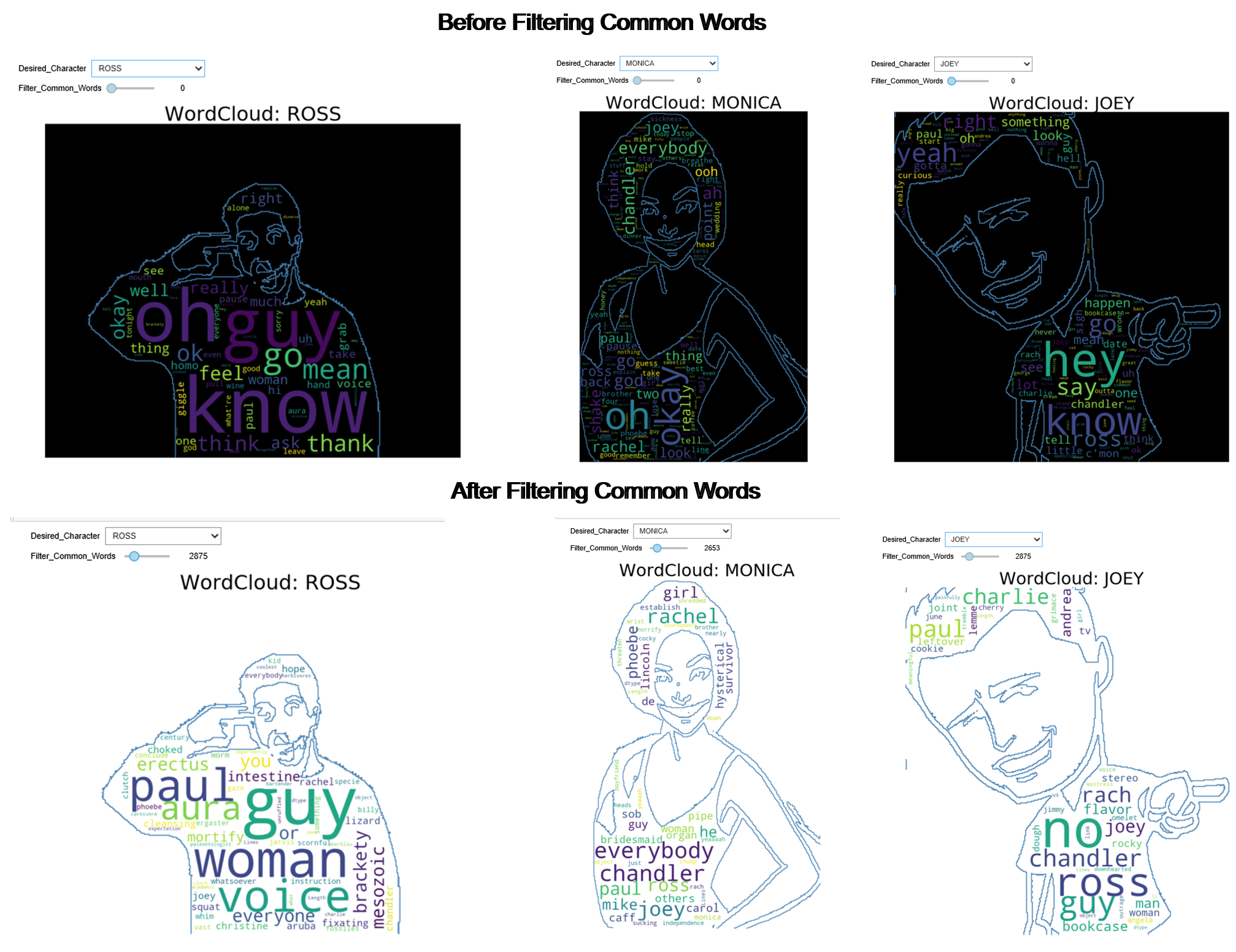
I generated wordclouds to check if it can be used to find words that are unique to different characters. For example, when I think of Ross, I always relate him to paleontology. So I wanted to check if a worldcloud for Ross would be able to relate him to paleontological terms. I decided to make the wordcloud interactive so that I can filter out the most frequent words that have been said by everyone in the show.For example, few of the commonly used words are oh, go, know, okay, start, really etc. When we generate a wordcloud using lines for Ross/Monica/Joey and set the filter to 0 (see figure below), the wordclouds are dominated by the similar common words. If we filter the first ~3000 common words using the slider, the wordcloud becomes more unique to the lines of Ross/Monica/Joey we know from the show [e.g. Mesozoic, aura, fossils etc for Ross, Chandler, Cookie, TV for Joey etc. after filtering 3000 common words].
Modeling Approach
The ML modeling for this problem is a multi-class classification task. While I explored the problem from classifying upto 15 members, to simplify this discussion, this blog only have results for the leading 6 characters.
Before ML modeling, differnt word embedding techcniques (i.e. tfidf, count -vectorizer and word2vec) were applied to convert the text into features. To identify the best word embedding technique, I applied a logisitic regression model for all of them and compared the accuracies. I picked tfidf for rest of the modeling steps as it resulted in the same accuracy as word2vec and is also computationally less expensive.
Below are the preliminary ML modeling results for different linear ML models after processing the lines with tfidf. All the ML models were found to have better prediction compared to the baseline model (i.e. a dummy classifier), however the overall accuracy for all ML models (multinomial naive bayes, logistic regression, SVC) are fairly low.

It is to note that while mean accuracy reflects the overall prediction ability of a classifer, it does not evaluate the degree to which a classifier can discriminate between different classes. In general, roc_auc score is a better representation of a classifier’s performance than accruacy for a multiclass problem as unlike accuracy, roc_auc does not depend on a specific thresholding value and evaluate the degree to which a classifier correctly identify different classes in a multiclass problem. Therefore, I will consider model performance in terms of macro roc_auc score in addition to mean accuracy to discuss improvement in the next section.
Feature Engineering and Resampling to Improving Model Prediction
There are few options that can be attempted to improve prediction by the models.
- A. We can take a look at the confusion matrix to check if the model in confusing any particular class with another and if there is a way to improve the distinction between the classes via feature engineering.
- B. As showed earlier in the barplot, there is a class imbalance in the data. While this imbalance is more significant between the 6 leading actors and the others, resampling can help adjust the imbalance in the data among the leading actors too and slightly improve the score.
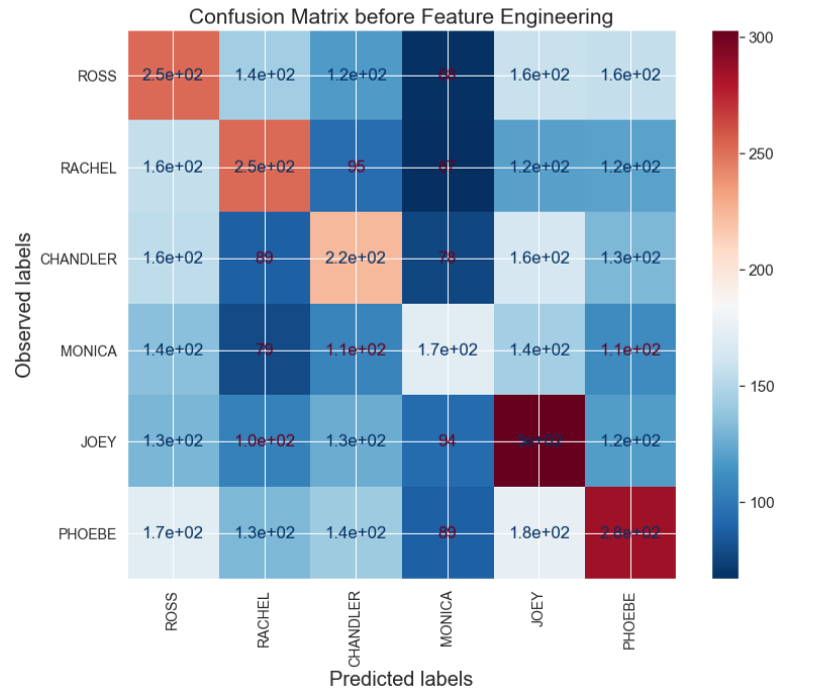
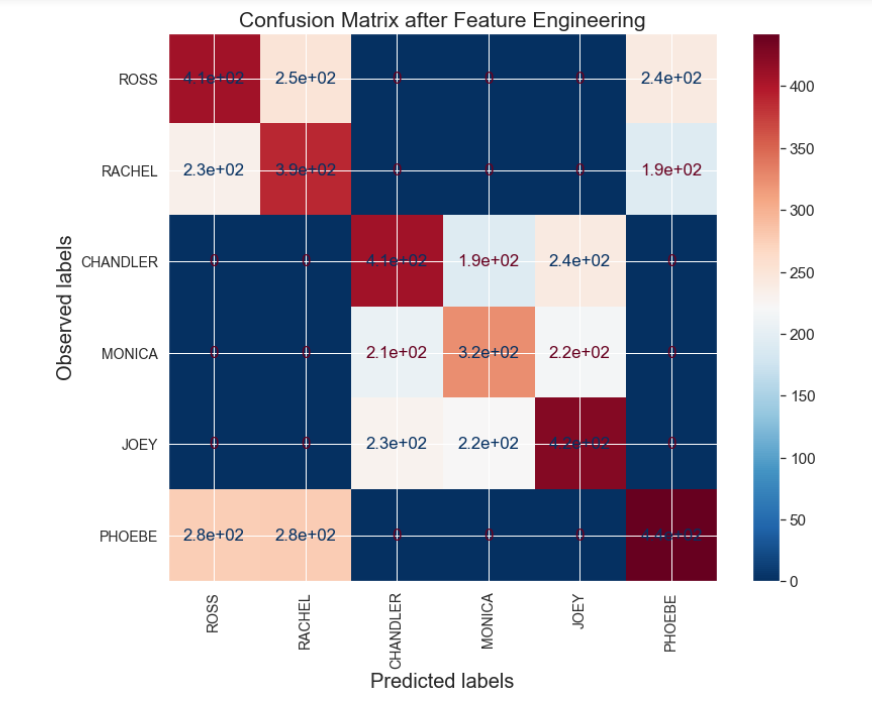
Above is a confusion matrix after making predictions with logistic regression after tuning the modeling parameters with gridsearch. The accuracy and macro roc_auc score obtained for this model were 0.26 and 0.64. The confusion matrix shows that the model has the highest probability of misclassifying Ross as Phoebe, Rachel as Ross or Monica ar Ross or Joey. Therefore, one way to help the model classify the characters better can be is to provide an extra input feature that lists the gender of the characters. When this was done and the logistic regression model was retrained, the accuracy and macro_roc_auc score for prediction on the test data was improved to 0.42 and 0.85.
To address class imbalance, both oversampling and undersampling techniques can be attempted for resampling. Both methods involve introducing a bias to select more samples from one class than from another, to compensate for an imbalance that is present in the data. As the name suggests, undersampling remove samples from over-represented classes and oversampling add more samples from the under-respresnted class in the raw dataset so that the dataset for modeling can have a balanced distribution of all classes. Whether an undersampling or oversampling scheme would work better for a dataset depends on the size of the train dataset that a particular classifier may require to be able to make a good prediction.
For this problem, I utilized random oversampling algorithm to resample the input data (‘Gender’ and ‘Lines’), and this further improved the classification accuracy to 0.46 and macro_roc_auc score to 0.86.As evident from the confusion matrix shown below,after feature engineering and oversampling, model now identify each class more distinctively. For example, it no longer misclassify ‘Ross’ as Chandler, Joey or Monica.